What's the Difference Between Annuity Types? A Guide to Choosing the Right One

What's the Difference Between Annuity Types? A Guide to Choosing the Right One
Introduction: Beyond the Basics - Choosing the Right Annuity Type for You
You've grasped the fundamental concept: annuities are structured periodic cash flows that can help secure your financial future. But here's where it gets interesting—the term "annuity" actually encompasses a diverse family of financial products, each designed for different needs and circumstances.
Consider this: Why do some annuities start paying you immediately while others make you wait years? Why do some guarantee a fixed return while others fluctuate with market performance? And most importantly, which type aligns with your specific retirement goals?
These aren't just academic questions—they're the key to making smart financial decisions. This comprehensive guide will demystify the various annuity types, explain how they work, outline their advantages and disadvantages, and provide you with a clear framework for choosing the right annuity to support your retirement planning goals.
Classification 1: By Payout Timing
Immediate Annuities
What they are: Immediate annuities are like converting a lump sum into an instant paycheck. You make a single, substantial payment to an insurance company, and they begin sending you regular payments almost immediately—typically within a month to a year.
How they work: Think of it as purchasing a personal pension. You're essentially trading a large chunk of money today for the guarantee of steady income tomorrow. The insurance company takes your lump sum, invests it, and uses actuarial tables to calculate how much they can pay you regularly while still making a profit.
Perfect for:
- Recent retirees who need to convert their 401(k) or pension lump sum into immediate living expenses
- Individuals who've received a windfall (inheritance, insurance settlement, or severance package) and want guaranteed income rather than investment uncertainty
- People who prioritize predictability over potentially higher returns
Pros and cons:
- Advantages: Provides immediate, predictable income with no investment decisions required. You'll know exactly how much you'll receive each month, making budgeting straightforward.
- Disadvantages: Once you commit, that money is typically gone—you've traded liquidity for security. If you need access to your principal for emergencies, you're generally out of luck.
Deferred Annuities
What they are: Deferred annuities are the "save now, pay later" option of the annuity world. You invest money today (either as a lump sum or through regular contributions), but the income payments don't begin until a future date you specify.
How they work: These annuities operate in two distinct phases. During the accumulation phase, your money grows through investments or guaranteed interest rates. During the payout phase (which might start 10, 20, or even 30 years later), you begin receiving regular payments.
Perfect for:
- Working professionals who want to supplement their 401(k) and IRA retirement savings
- Individuals seeking potential tax advantages (earnings grow tax-deferred in many jurisdictions)
- People who have time before retirement and want their money to grow before they need income
Pros and cons:
- Advantages: Time is your ally—compound growth can significantly increase your eventual payouts. Many offer tax-deferred growth, meaning you don't pay taxes on gains until you withdraw.
- Disadvantages: More complex than immediate annuities, often with surrender charges if you need early access to funds. The longer time horizon also means more variables that could affect your final outcome.
Classification 2: By Rate of Return Type
Fixed Annuities
What they are: Fixed annuities are the "savings account on steroids" of the annuity world. They offer a guaranteed, predetermined interest rate for your money, providing completely predictable growth and income.
How they work: Similar to a bank certificate of deposit (CD), but typically offering higher rates and issued by insurance companies rather than banks. Your principal is protected, and you earn a stated interest rate regardless of market conditions.
Perfect for:
- Risk-averse investors who prioritize capital preservation over high returns
- People nearing retirement who want to lock in a portion of their assets at a guaranteed rate
- Individuals who lose sleep over market volatility and prefer certainty
Pros and cons:
- Advantages: Complete predictability—you know exactly what you'll earn. Your principal is typically guaranteed by the insurance company's financial strength.
- Disadvantages: Lower potential returns compared to market-based investments. In periods of high inflation, fixed returns might not maintain your purchasing power over time.
Variable Annuities
What they are: Variable annuities are like having a 401(k) wrapped in an insurance product. Your money is invested in sub-accounts that resemble mutual funds, and your returns depend entirely on how these investments perform.
How they work: You choose from a menu of investment options—typically stock funds, bond funds, and money market accounts. Your annuity value rises and falls with the performance of your chosen investments, just like a regular investment portfolio.
Perfect for:
- Investors comfortable with market risk who seek higher long-term returns
- People with long investment horizons who can weather market volatility
- Individuals who want to maintain some control over their investment allocation
Pros and cons:
- Advantages: Potential for higher returns that can outpace inflation. You maintain some investment control and can potentially benefit from strong market performance.
- Disadvantages: Your principal and returns are at risk—you could lose money. These products often come with higher fees than other annuity types, which can eat into returns.
Indexed Annuities
What they are: Indexed annuities are the "have your cake and eat it too" option. They offer the potential for market-linked gains while protecting your principal from market losses. Your returns are tied to a market index (like the S&P 500) but with built-in safeguards.
How they work: These products typically offer a guaranteed minimum return (the "floor") while capping your maximum gain (the "cap"). If the index performs poorly, you still earn the minimum. If it performs well, you participate in the gains up to the cap limit.
Perfect for:
- Moderate risk-takers who want market upside potential without the full downside risk
- Investors seeking better returns than fixed annuities but with more protection than variable annuities
- People who are intrigued by market participation but need principal protection for peace of mind
Pros and cons:
- Advantages: Upside potential with downside protection. Your principal is typically guaranteed while still allowing for market-linked growth.
- Disadvantages: Complex products with caps that limit your upside potential. Returns may lag in strong bull markets due to participation rate limits and caps.
Other Important Annuity Types & Features
Life Annuities
What they are: Life annuities are your insurance against outliving your money. They guarantee payments for as long as you live, regardless of whether that's 5 years or 50 years after you start receiving payments.
Key benefit: They solve the "longevity risk" problem—the fear that you'll live longer than your money lasts. This is particularly valuable as life expectancies continue to increase.
Period Certain Annuities
What they are: These annuities pay for a specific period (such as 10, 20, or 30 years) regardless of whether you're alive. If you die before the period ends, your beneficiaries continue receiving payments.
When they make sense: Ideal for people who want guaranteed income for a specific time period or who want to ensure their beneficiaries receive something even if they die early.
Joint and Survivor Annuities
What they are: Designed for couples, these annuities continue paying as long as either spouse is alive. When one spouse dies, payments typically continue to the survivor (sometimes at a reduced amount).
Perfect for: Married couples who want to ensure the surviving spouse maintains income security throughout their lifetime.
Ordinary Annuity vs. Annuity Due: A Quick Refresher
Here's where our annuity calculator's "Payment Timing" option becomes crucial:
- Ordinary Annuity: Payments occur at the end of each period (end of month, quarter, or year)
- Annuity Due: Payments occur at the beginning of each period
This timing difference might seem minor, but it significantly impacts the present and future value calculations. When using financial calculators or planning tools, make sure you select the correct payment timing to get accurate projections.
How to Choose the Right Annuity for Your Retirement Plan
Selecting the right annuity isn't about finding the "best" product—it's about finding the best fit for your unique situation. Here are the key questions to ask yourself:
Key Decision Questions
What's your risk tolerance?
- Low risk tolerance → Fixed annuities
- Moderate risk tolerance → Indexed annuities
- High risk tolerance → Variable annuities
When do you need income?
- Need income now → Immediate annuities
- Need income in the future → Deferred annuities
Are you concerned about inflation?
- Yes → Consider variable or indexed annuities that can potentially grow with the economy
- No → Fixed annuities might suffice
Do you need to provide for a spouse?
- Yes → Joint and survivor annuities ensure continued income for your spouse
- No → Single life annuities typically offer higher payment rates
A Simple Decision Framework
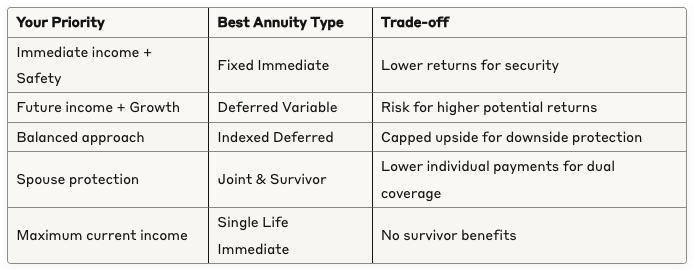
Consider Your Complete Financial Picture
Remember, annuities shouldn't exist in isolation. Consider how they fit with your other retirement assets:
- Social Security: Provides inflation-adjusted lifetime income
- 401(k)/IRA: Offers flexibility and potential growth
- Annuities: Can fill gaps by providing guaranteed income or additional tax-deferred growth
A well-rounded retirement plan might include fixed annuities for essential expenses, variable investments for growth potential, and liquid savings for emergencies.
Conclusion: No "Best" Annuity, Only the "Right" Annuity for You
The annuity landscape offers something for almost every retirement planning need, from the security-focused retiree seeking guaranteed income to the growth-oriented investor looking for tax-deferred accumulation. The key is matching the product characteristics with your specific goals, risk tolerance, and timeline.
Remember that annuities are long-term commitments with significant financial implications. Take time to understand the fees, surrender charges, and terms before committing. Consider working with a qualified financial advisor who can help you evaluate how different annuity types fit into your overall retirement strategy.
Ready to explore your options? While commercial annuity products can be complex, you can start by using our annuity calculator to model basic fixed annuity scenarios. Experiment with different interest rates, time periods, and payment timings to see how these variables impact your potential future income. Understanding these fundamental relationships will help you make more informed decisions when you're ready to explore actual annuity products.
Start planning your financial future today—because the best annuity is the one that helps you sleep well at night while building the retirement you deserve.